Saturday, February 1, 2020
|| MOMO Achar Recipe || Easy momo pickle recipe ||
What is MOMO ACHAR?
Momo is a nepali steamed dumplings commonly eaten in most of the parts in nepal.MOMO is stuffed with various types of stuffings like veggies,chicken,mutton,paneer,mushroom,buff.In nepal buff(Buffalo) stuffing is most popular.A momo achar is a spicy semi-liquid saucy dipping which helps to enhance the taste of the momo.MOMO achar plays key role to determine the taste of the momo.So,lets start with the ingredients required for the momo achar.
Ingredients
- Tomatoes
- salt
- chili powder
- peanuts
- soybeans
- water
- coriander leafs
- Turmeric powder
- Cumin seeds
- Lemon juice
- Sesame
- ginger
- garlic
Steps To Follow
- On a dry pan roast some peanuts and soybeans and sesame one by one.
- Again heat up oil and fry cumin seeds.After cumin seeds turn brown fry green chilies ginger and garlic and add turmeric powder.
- Add chopped tomatoes on the pan and mix the tomatoes well.
- After mixing the tomatoes add salt to the mixture and close the lid of he pan for a while.
- After few minutes the tomatoes might have started to form a semi-liquid.
- Add coriander leafs and let the mixture rest for a while.
- Take a mixture-grinder and add tomatoes mixture with roasted soybeans,peanuts and sesame.
- Mix the mixure very well and the mixture is ready to serve with hot momos.
Watch this video for some help regarding the recipe
Video source:Yummy Food World
Keywords of the article:
momo achar
momo achar recipe
momo achar tutorial
momoi acchar recipe
how to make momo achar
momo achar kasari banaune
momo sauce
momo sauce recipe
momo sauce tutorial
how to make momo sauce nepal
momo achar nepali recipe
nepali momo achar
saabkura momo
achar recipe
momo achar easy methos
momo
achar
momo achar in nepal
tasty momo achar
tasty momo sauce
thick momo achar
momo serving nepal
Friday, January 31, 2020
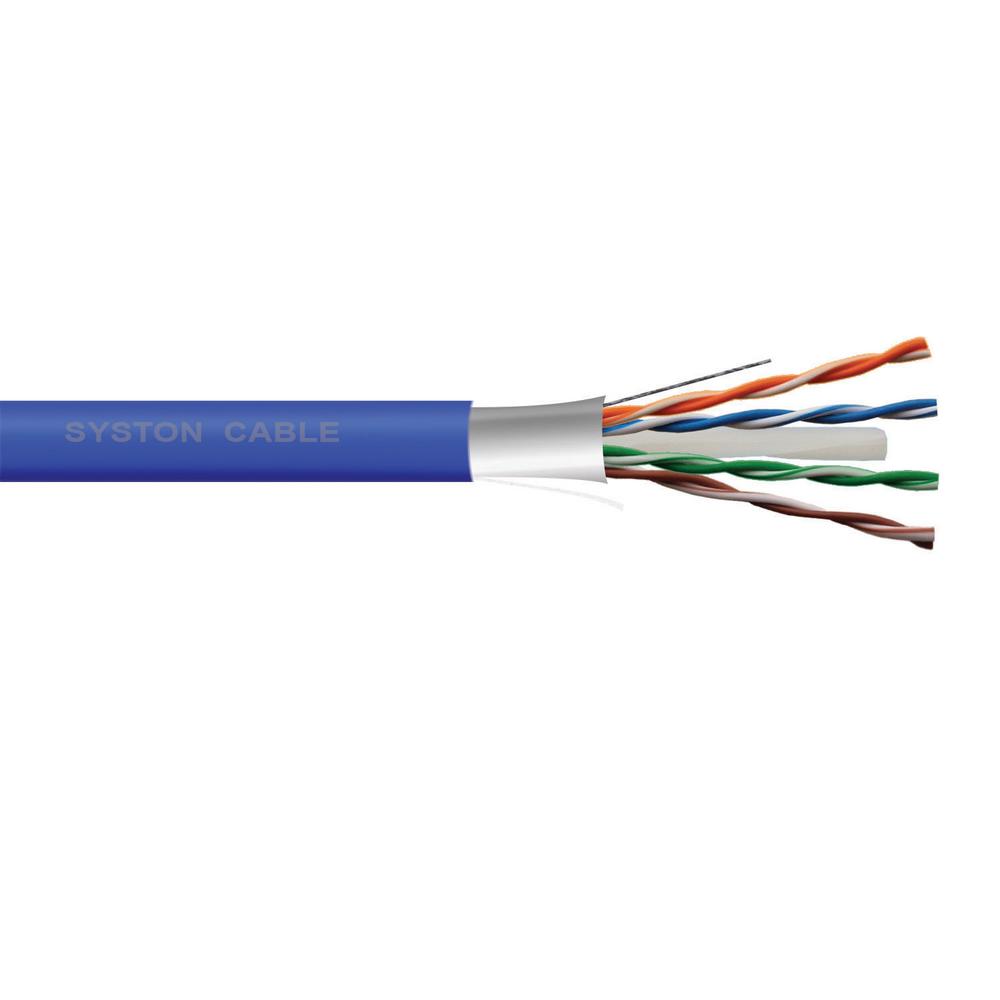
Types of cables in guided media
Twisted-Pair cable
- It consists of four pairs of copper wires coated with an insulating materials like plastic or teflon and twisted together.
- It is often used data network for short and medium length connections because of it's relatively lower cost compared to optical fiber and co-axial cable.
- Twisted pair cables are of two types:
- Shielded twisted pair cable (STP)
- Shielded twisted pair cables (STP) is similar in construction to un-shielded twisted-pair cabled wire (UTP) except that twisted pair is enclose in a woven copper for providing extra protection from external interference.
- It is expensive then UTP.
- Transmission speed is upto 500 mbps at 100m range.
- Un-Shielded twisted pair cable (UTP)
- UTP cable consists of number of twisted pairs of wires with a simple plastic casing.
- It is commonly used in telephone line system.
- The commonly used UTP cable is Category 5 cable (Cat 5) which is used with fast ethernet.
Coaxial Cable
- A coaxial cable has a single inner conductors that transmits electric signals,the outer conductor act as a ground,the two conductors are separated by insulation.The inner conductor,insulator and the outer conductor are wrapped in a sheath of teflon or pvc.
- The copper wire is used for both inner and outer conductor,the signal is transmitted over the surface of inner conductors.
- A thicker coaxial cable can transmit more data than thinner one.
- The commonly used coaxial cable is telephone trunklines, broadband internet networking cables, high speed computer data busses, carrying cable television signals, and connecting radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas.
Optical Fiber
- Optical fiber, refers to the medium and the technology associated with the transmission of information as light pulses along a glass or plastic strand or fiber. A fiber optic cable can contain a varying number of these glass fibers -- from a few up to a couple hundred.
- It has high bandwidth and faster speed.
- It's flexibility is generally high.
- It helps in secure transmission process.
- It is commonly used in surgery and dentistry,lighting and decoration and mechanical inspections.
Number system || chapter two BCA TU || Digital logic
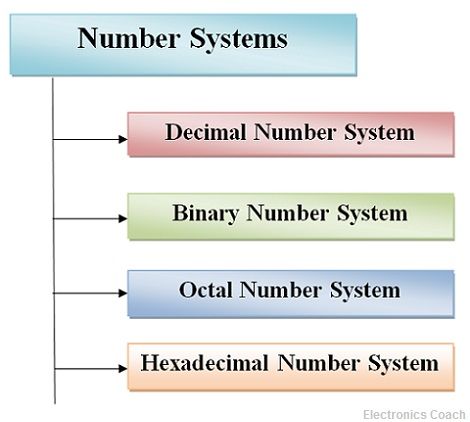
Number system
A number system in base r or radius r uses unique symbols for r digits. One or more digits are combined to get a number.In computers, we are concerned with four kinds of number systems, as follows:
Decimal Number System ------------ Base 10
Binary Number System ------------ Base 2
Octal Number System ------------ Base 8
Hexa-Decimal Number System -------- Base 16
Decimal Number System
It consists of 10 digits (0-9).
Binary Number System
It consists of 2 digits (0-1).
Octal Number System
It consists of 8 digits (0-7).
Hexa-Decimal Number System
It consists of 16 digits (0-9 and A-E) whereas from digit 10 it is named after alphabets A that means A is number 10 and E is number 15.
Conversion of Decimal to Binary, Octal, Hexa-decimal
binary-divide by 2, for fraction multiply by 2
octal-divide by 8, for fraction multiply by 8, and,
hexadecimal-divide by 16, for fraction by 16.
Conversion of Binary to Decimal, Octal, Hexadecimal
decimal-multiply by 2 with the power of their descending position and for fraction with power of their ascending position but with negative sign in powers.
octal-multiply by 8 with the power of their position and for fraction with the power of negative sign.
hexadecimal-multiply 16 with the power in it and negative for fraction.
Conversion of Binary to Octal, Hexa-Decimal
8= that means while converting binary digits to octal we have to arrange three digits of binary number starting from last position to get octal number.
16= that means while converting binary digits to hexadecimal we have to arrange four digits of binary number starting from last position to get octal number.
Conversion of Octal, Hexadecimal to Binary
As said above each number of octal number equals to three digits of binary number i.e. final binary number will be combination of each number formed while converting.
Convert each hexadecimal digit to four digits of binary number and the combination of all digits will be the final conversion.
Radix Complement
The r's complement of "n" digit, number "N" in base "r" is defined as -N for N=0 and 0 for N=0.
Comparing with (r-1)'s complements the r's complement is obtained by adding 1 to the (r-1)'s complement since -N= [(-1)-N] +1.
Binary Arithmetic
Binary Addition
Binary Subtraction
Binary Multiply
Binary Divide
Binary Addition
The Addition of the Binary numbers involve the following steps:
Start addition by adding the bits in unit column (the right-most column).
The result of adding of a column is a sum with or without a carry.
Write the sum in the result of that column.
If a carry is present, the carry is carried over to the addition of the next left column.
Binary Subtraction
The steps for performing subtraction of the binary numbers are as follows: -
Start subtraction by subtracting the bit in the lower row from the upper row, in the unit column.
Use the binary subtraction rules. If the bit in upper row is less than lower row, borrow 1 from the upper row of the next column (on the left side).
Rule of subtraction
1-1=0 0-1=1 (borrowed 1 from upper one)
Binary Multiply
Rules for Binary Multiply: 1*0=0 1*1=1
Binary Division
Binary number is divided same as dividing decimal number.
Binary Coded Decimal (BCD)
In this code each digit is responsible by a 4-bit binary number. The positional weight is assigned to the binary digits in BCD code are 8-4-2-1 with 1 corresponding to LSB and corresponding MSB.
Positional 8 4 2 1
Weight
While converting from BCD to binary, convert same as converting binary.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001
Invalid BCD Codes
with 4-bits we can represent total 16 numbers (0000 to 1111) in BCD only first ten codes on used (0000 to 1001)
Therefore, remaining six-codes (1010 to 1111) are invalid in BCD.
The binary coding schemes that are mostly used are: -
Extended Binary Code Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC)
American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)
Unicode
EBCDIC
The Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBDIC) uses 8 bits (4 bits for zone, 4 bits for digit) to represent a symbol in the data.
EBCDIC allows = 256 combinations of bits.
256 unique symbols are represented using EBCDIC code. It represents decimal numbers (0-9) lower case letters (a-z), upper case letters (A-Z), Special characters, and Control characters (printable and non-printable, e.g., for cursor movement, printer vertical spacing, etc.
EBCDIC codes are mainly used in the mainframe computers.
ASCII
The American Standard Code for Information interchange (ASCII) is widely used in computers of all types.
ASCII codes are two types- ASCII-7 and ASCII-8.
ASCII-7 is a 7-bit standard ASCII code. In ASCII-7, the first 3 bits are the zone bits and the next 4 bits are for the digits. ASCII-7 allows = 128 combinations. 128 unique symbols are represented using ASCII-7 has been modified by IBM to ASCII-8
ASCII-8 is an extended version of ASCII-7. ASCII-8 allows =256 combinations. ASCII-8 represents unique symbols. ASCII-8 is an 8-bit code having 4 bits for zone and 4 bits for the digits. ASCII is widely to represent data in computers.
Code 0-31 used for actions like Carriage Return (CR), Bell (BEL), etc.
Code 48-57 for numeric
Code 65-90 for uppercase letters
Code 97-122 for lowercase letters
Code 128-255 are extended ASCII codes.
Unicode
It is a universal character encoding standard for the representation of text which includes letters, numbers and symbols in multi-lingual environments. The Unicode Consortium based in California developed the Unicode standard.
It uses 32 bits to represent a symbol in the data.
It allows =4164895296 (~ 4 billion) combinations.
It can uniquely represent any character or symbol present in any language. In addition to the letters; mathematical and scientific symbols are also represented in Unicode.
It is compatible with the ASCII-8 codes. the first 256 codes are identical to the ASCII-8 codes.
Gray Code
It is also known as Reflected Binary Code is defined as an ordering of the binary number system such that each incremental value can only differ by one bit. I n gray code, whole traversing from one step to another step only one bit in the group changes. That is to say that two adjacent code numbers differ from each other by only one bit.
Gray code is the most popular of the unit distance code, but it is not applicable for Arithmetic Operations. Gray Code has some application is Analog to digital Convertors, as well as used for error correction in Digital Communication.
Excess-3 Code
It is basically a binary code which is made by adding 3 with equivalent decimal of binary number and again converting it into binary number. So, if we consider any binary number we have to first convert it into decimal number then add 3 with it and then convert into binary.
Self-complementing Property:
Excess-3 code is non-weighted and self-complementary code. A self-complementary binary code is always complemented themselves. The compliment of a binary number can be obtained from that number by replacing 0's with 1's and 1's with 0's. The sum of binary number and its complement is always equal to decimal 9. In other words, the 1's complement of an excess-3 code is the excess-3 code for the 9's complement of the corresponding decimal number.
Alpha-numeric Codes
A binary bit can represent only two symbols '0' and '1'. But it is not enough for communication between two computers because there we need many more symbols for communication.
These symbols are required to represent:
26 numbers with capital and small letters
Number 0 to 9
Punctuation marks
Alpha-numeric codes represent numbers and alphabetic characters. They also represent other characters such as punctuation symbols and instructions for conveying information.
Boolean algebra and logic gates
The most common postulates used to formulate various algebraic structures are:
Associative law: A binary operator * on a set S is said to be associative whenever:
(x*y) *z=x*(y*z)
Commutative law: A binary operator * on a set S is said to be commutative whenever:
x*y=y*x
Identity element: A set S is said to have an identity element with respect to a binary operation * on S if there exists an element eS with the property:
e*x=x*e=x for every xS
Inverse: A set having the identity element e with respect to a binary operator * is said to have an inverse whenever, for every xS, there exists an element yS such that:
x*y=e
Distributive law: If * and · are two binary operators on set S, * is said to be distributive over* whenever:
x*(y*z) =(x*y) *(y*z)
Theorem 1(a): x+x=x
Theorem 1(b):x*x=x
Theorem 2(a):x+1=x
Theorem 2(b):x*0=0
Theorem 3 :(x') '=x
Theorem 6(a):x+yx=x
Theorem 6(b):x(y+x)=x
Thursday, January 30, 2020
Bhang ko achar recipe hemp seed pickle
How to make bhang ko achar nepali recipe
Generally,in our society we consider bhang(hemp seed) as a psychoactive drug but in this recipe we are using just seeds of bhang which is totally safe to use and it won't show any effects that a psychoactive drugs would show.You can have bhang ko achar with your regular launch and dinner and in any time of your day.Let's start the procedure to make bhang ko achar.
Ingredients
- Coriander
- Dried red chilies
- Red chili powder
- Turmeric powder
- Salt
- Lemon juice
- Chopped ginger
- Garlic
- Chopped green chilies
- Fenugreek (METHI)
- Bhang seeds (Hemp seeds)
- Chopped Onions
- Boiled Potatoes
- Mustard Oil
Steps To Follow
- In a dry pan fry bhang seeds (Hemp seeds) after the seeds start to pop turn off the heat and it is ready for use let it rest for a bit in a normal room temperature.
- After the seeds dry crush it into the powder.
- Now,make ginger garlic paste and lets jump into another step.
- Take a big bowl where you can mix every items perfectly.
- Add boiled potatoes,grinded bhang seeds,green chili powder,salt,chopped green chilies,chopped onions.
- Again,heat up the pan and put mustard oil and methi and dried chilies on the oil.
- When the chilies and methi turns black add turmeric powder and pour it into the bowl where we mix our ingredients.
- In the bowl add some lemon juice,chopped coriander and mix all ingredients finely.\
- After mixing it well it is ready to serve.
Watch this video for some help:
video source:Yummy Food World
Keywords:
bhang ko achar
hemp seed pickle
how to make bhang ko achar
how to make hemp seed pickle
bhang pickle
bhang ko achar nepali recipe
bhang ko achar recipe
bhang ko achar easy recipe
bhang ko achar process
aloo and bhang
potatoes pickle nepal
easy nepali pickle recipe
bhang pickle nepal
hemp seed pickle in nepal
potatoes pickle nepal
hemp in nepal
what is bhang ko pickle
bhaang ko pickle
bhang ko acchar
bhang achar
bhang pickle
bhang achar nepal
bhang pickle nepal
bhang achar tutorial
bhang achar tutorial
saabkura bhang
sabkura bhang
sabkura hemp
nepali bhang ko achar
Wednesday, January 29, 2020
Corona virus in Nepal symptoms and history
कोरोना भाइरस
चीन बाट सुरु भएको corona virus फैलिने क्रम मा अमेरिका सम्म पुगिसकेको छ | होंग्कोंग ,जस्ता देश हरु मा पनि corona virus तिब्र रुप ले फैलिरहेको छ | Corona virus स्वास प्रसाश मा भाग लिने अंग हरु मा प्रतक्ष्य आशार पर्ने virus हो | पहिले यो virus जनावर मा मात्र देखिने गरेको थीयो तर २०१२ मा पहिलोपटक यो virus साउदी अरब ,अफ्रीका र एशिया का केहि मुलुकहरुमा साधारण रुप मा देखापरेको थीयो
हालै चीनको wuhan प्रान्त बाट फैलिएको यो corona virus बाट हाल सम्म १०६ जना को मृत्यु वैसकेको छ भने ४५०० जना भन्दा बढी मा एसको संक्रमण देखापरिसकेको छ | यो virus को लक्ष्यण ज्वरो आउनु ,स्वस्प्रसस मा समस्या देखा पर्नु र नेमोनिया को लक्ष्यण देखा पर्नु हुन् |
यो virus ले फोक्सो को ठुलो भाग मा असर गरि नेमोनिया को बिकाश गर्छ अन्य संक्रमण मा भन्दा corona virus मा नेमोनिया बिकाश गर्ने सक्ति बढी हुन्छ | जनावर बाट सर्ने भनिएको यो virus आहिले मनिष बाट मनिष मा अत्ध्यधिक मात्रा मा फैलिदै गैराखेको छ |
नेपाल मा पनि corona virus देखा परेको पुस्टि भएको छ | चीन बाट नेपाल आएका एक बिद्यार्थी को स्वस्थ परिक्षण गर्दा यो संक्रमण को पुस्टि भएको स्व्यास्थ तथा जनसंख्या मन्त्रालय ले शुक्रबार पत्रकार सम्मेलन गरि जानकारी गराएक थीयो | corona virus नेपाल भित्रिन नदिन त्रिभुवन अन्तर्राष्ट्रिय विमानस्थल मा हेअल्थ डेस्क पनि स्थापना गरिएको छ | हेअल्थ डेस्क मा संक्रमण फैलिएका मुलुक बाट आएका पर्यटक तथा नेपालीले अनिवार्य स्व्यास्थ परिक्षण गर्नु पर्ने छ |
Transmission media and it's types (TU BCA NOTES)
Transmission Media
- Transmission media the pathway network entities used to connect each other.
- Computer transmission media includes
- guided media
- unguided media
- Guided media transmits signals by sending electricity or light over a cable or wire
- It uses a cabling system that guides the data signals along a specific path.
- The data signals are bounded by the cabling system so it is also called bounded media.
- Examples:twisted-pair wire,co-axial cable,fiber optics cable.

- Un-guided transmission media consists of a means for the data signals to travel but nothing to guide that along a specific path.
- It transmits data through the open air.
- Examples: radio waves ,infrared signals and earth and satellite based microwaves.
How to make chatamari nepali food recipe
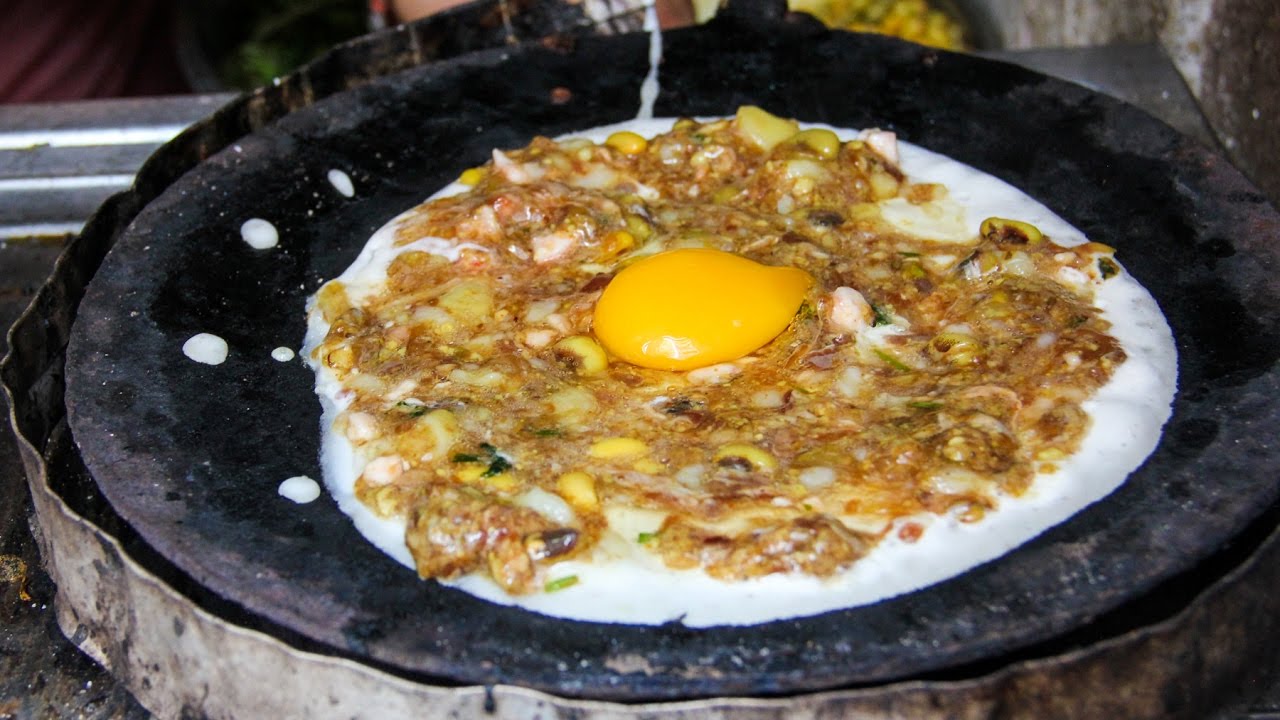 What is chatamari?
What is chatamari?
Chatamari is one of the easiest and one of the tastiest food made in nepal (specially in newar community) during special occasions.You can taste authentic chatamari in local restaurant's of kathmandu valley in any time of the year or you can visit during festive seasons.Ingredients:
- Water
- 3 eggs
- 300g chicken keema ( a type of filling with no bones)
- Rice flour
- Chopped coriander
- Chopped onions
- Chopped tomatoes
- Chilies
- Calt
- Ginger-garlic paste
- Cumin powder
- Coriander powder
Steps:
- Lets prepare batter for chatamari. Add rice flour in a bowl and slowly add water and keep mixing flour with water.Stir the batter for 3-4 minutes for perfect thickness.The batter should not be too thin nor too thick.
- On another side add chopped onions,tomatoes,coriander,ginger-garlic paste,salt,cumin and coriander powder,chopped chilies with three eggs in the chicken and mix well.
- Chatamari is made without oil so on a dry pan pour the flour batter making circular shape on a low heat.
- Add chicken stuffing on top of the flour batter in the pan and again break one egg on top of the flour in the pan with some sprinkle of salt.
- Close the pan with a lid and cook for 7-8 minutes.
- Now you can take out chatamari from the pan and have a taste of it.
If you have any doubts or confusions regarding the recipe you can freely contact our team.
THANK YOU
Tuesday, January 28, 2020
What is K-MAP and how to solve it|| KARNAUGH MAP || BCA TU NEPAL || Digital Logic ||
Karnaugh Map (K-MAP)
The K-MAP is a graphical representation that provides a systematic method for simplifying a boolean expression.
Two Variable K-MAP
For n variable k-map 2^n cells are required.Therefore for two variable k-map,2^2=4 cells are required.
 |
For constructing three variable k-map 2^3=8 cells are required.
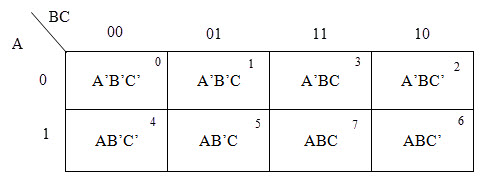
Four Variable K-MAP
For constructing four variable k-map 2^4=16 cells are required.
Why are K-MAPS used in boolean algebra?
Karnaugh's map are used to simplify real-world logic requirements so that they can be implemented using a minimum number of physical logic gates.K-MAP reduces the need for extensive calculations by taking advantage of human's pattern recognition capability
Grouping of cells for simplification in K-MAP
Adjacent cell's which have 1's can be grouped together in 2^n powert that is:
Two adjacent cells can be grouped together
Four adjacent cells can be grouped together
Eight adjacent cells can be grouped together
Sixteen adjacent cells can be grouped together
Rules followed for K-MAP simplification
So,these are the basic information about karnaugh's map if you have any problems or confusions regarding the topic feel free to contact us.
Wednesday, November 7, 2018
Advantages and disadvantages of market economy|
In our previous article we have discussed about the concept of market economy and its features.You had not read it press here to read it.In this article lets discuss some of the advantages and disadvantages of market economy.

1.Freedom for consumers
 One of the major disadvantages of market economy is that it creates gap between rich and poor in the society.Majority of the productive resources are captured by very few rich people.On the other hand,more people are surviving with very few resources.So,there is unequal distribution of income and resources in the country.
One of the major disadvantages of market economy is that it creates gap between rich and poor in the society.Majority of the productive resources are captured by very few rich people.On the other hand,more people are surviving with very few resources.So,there is unequal distribution of income and resources in the country.

Advantages of market economy.
1.Freedom for consumers
one of the advantages of market economy is that there is freedom for consumers in the market.Consumers can choose goods in several markets like in Nepal,China,India etc as per their interest,financial capacity and só on.They are free to purchase the number of goods as per their desire.
2.Mobility of factors of production
The next advantages of market economy is that factors of production are perfectly mobile i.e they can go from one place to another place if they get better opportunity there.For example-A lecturer of economics,who is working in littel angles college can go in new horizon college,global college etc,if he gets salary and other benefits over there.
3.perfect competition
The next advantages of market economy is that there exists perfect competition in both product and factor market.The prices of goods and services are determined with the help of market forces-demand and supply in respective market.
Disadvantages of market
1.creates Economic inequality
 One of the major disadvantages of market economy is that it creates gap between rich and poor in the society.Majority of the productive resources are captured by very few rich people.On the other hand,more people are surviving with very few resources.So,there is unequal distribution of income and resources in the country.
One of the major disadvantages of market economy is that it creates gap between rich and poor in the society.Majority of the productive resources are captured by very few rich people.On the other hand,more people are surviving with very few resources.So,there is unequal distribution of income and resources in the country.2.private sector domination
In market economy,majority of the economic activities and allocation of resources are carried by private sector.Government has very limited roles in this economy especially,maintaining law and order,printing money,providing public services,developing infrastructures,etc.
3.Profit motive
Market economy is dominated by private sector.They carry their economic activities being profit motive rather then service motive as their goal is profit maximization.
Subscribe to:
Comments
(
Atom
)